Gene Details: GNE
1 / 1
General Information
Gene Name: GNE (Bifunctional UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase)
Synonym: GLCNE
Short Names:
Alternative Names: UDP-GlcNAc-2-epimerase/ManAc kinase;
Notes:
- Bifunctional enzyme responsible for epimerization of UDP-GlcNAc to UDP-ManNAc, and the phosphorylation of UDP-ManNAc to UDP-ManNAc 1 phosphate.
- Dysfunctional GNE results in two disorders in Human: sialuria and GNE-myopathy. Sialuria is caused by the decreased feedback inhibition of GNE via the accumulation of CMP-sialic acids. GNE-myopathy is a late onset disease where muscle weakness manifests later in life. The molecular mechanisms are unclear, but increased sialic acid is observed in patients.
Description from Dr.Glyco-GPT:
Warning: LLMs can generate factually incorrect information, as they simply predict the next word based on training data. Always verify LLM output by cross-checking with reliable sources!
Catalytic Activity
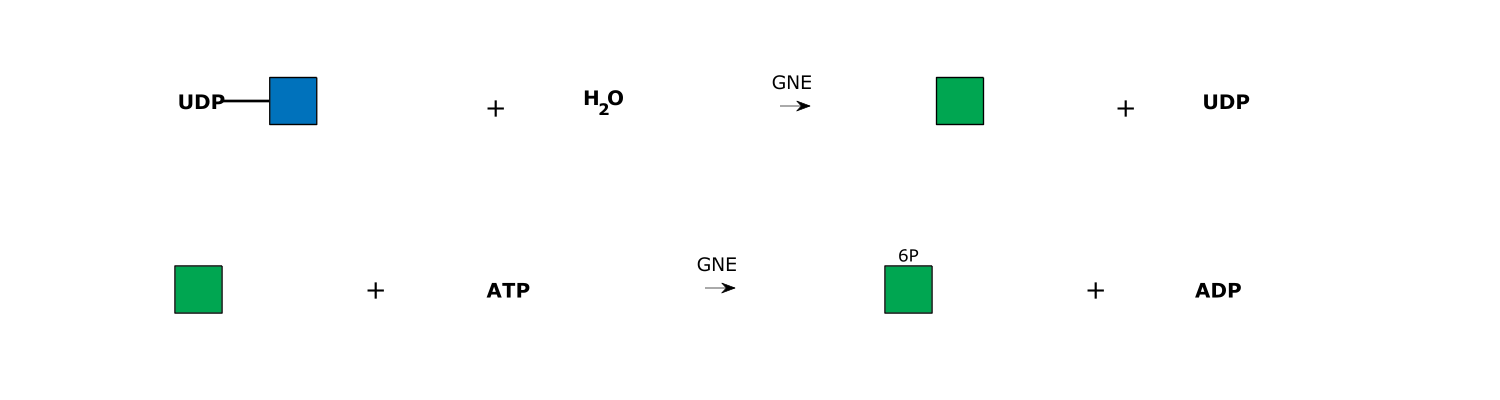
Reaction and Disease Links
KEGG: 10020
Transcript levels (Cell lines and Single cell data) URL
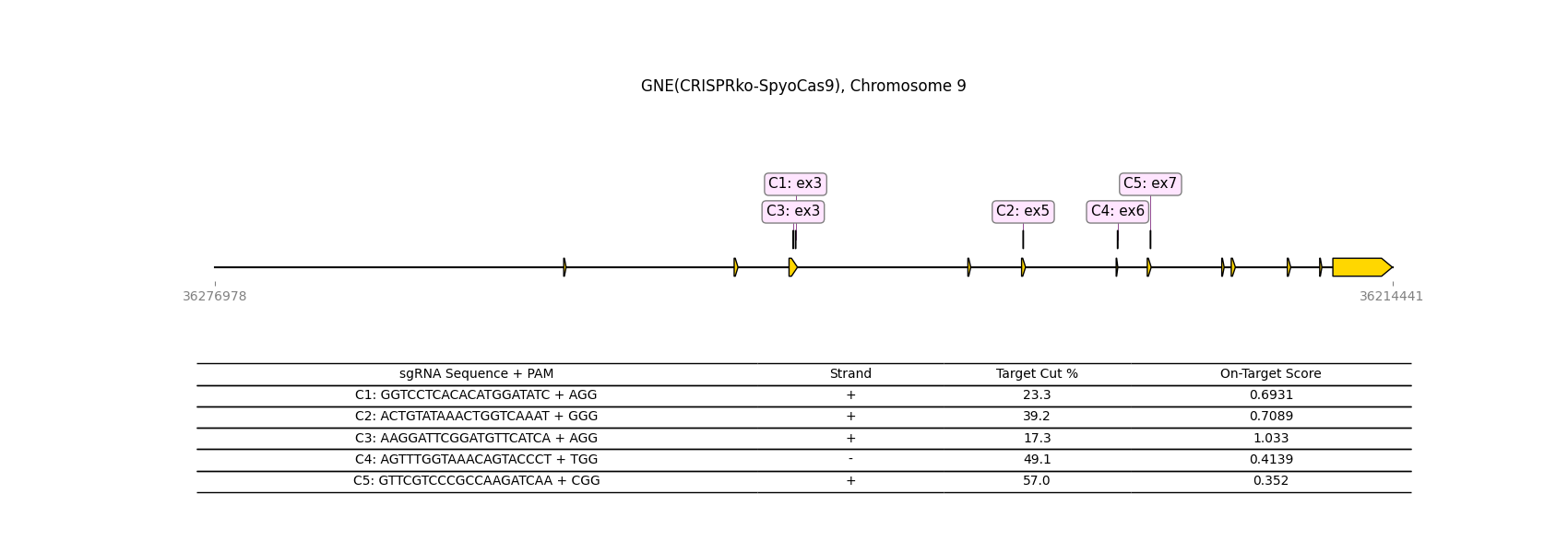
CRISPR-knockout
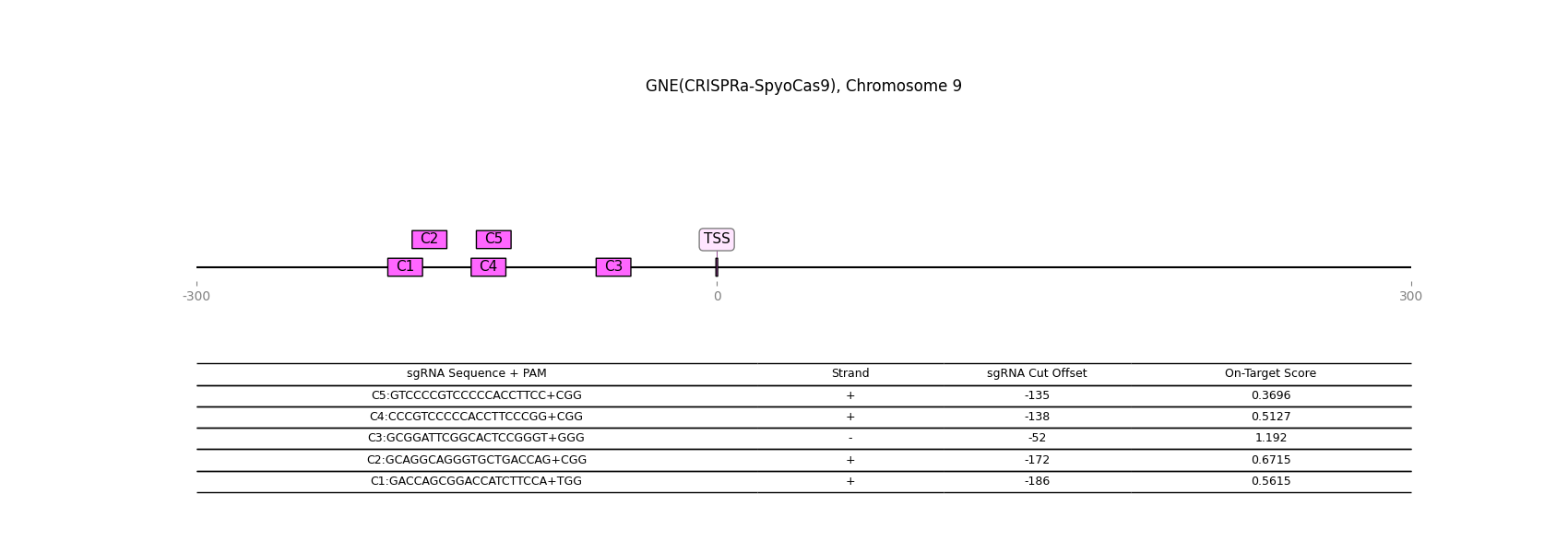
CRISPR-activation
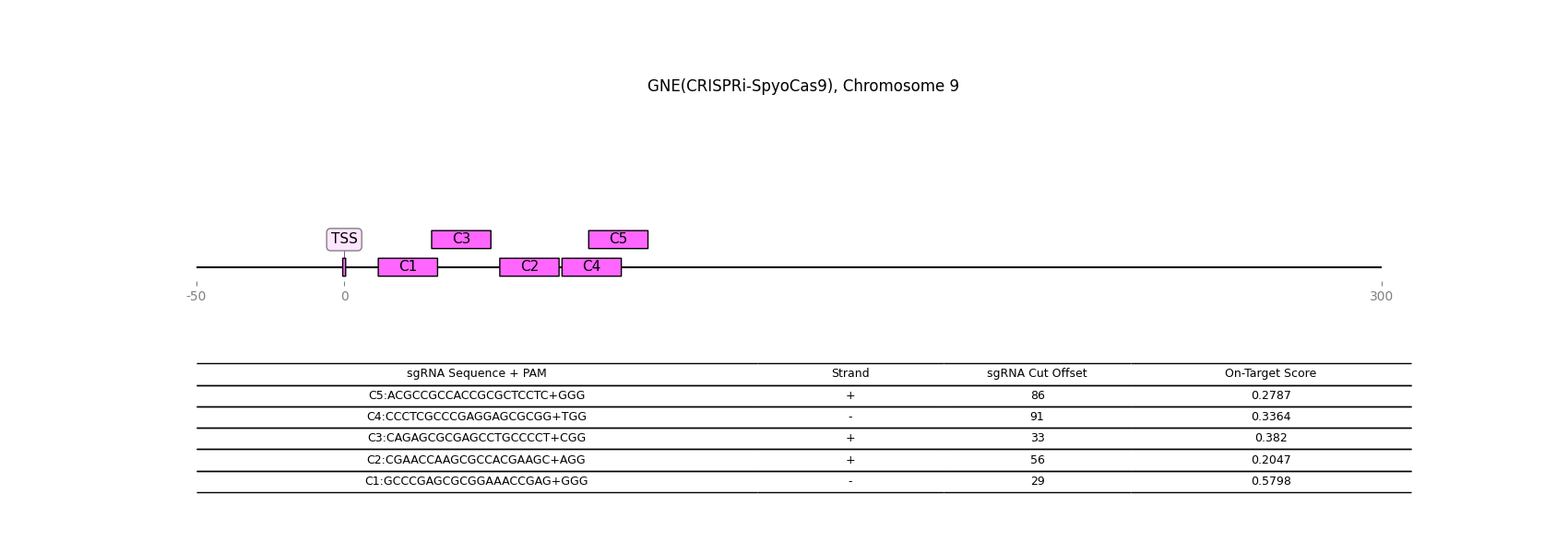
CRISPR-inactivation
Transcription factor-gene relationship (details at glycoTF page)
Top 10 TFs
| TF | Score |
|---|---|
| TCF25 | 0.349006 |
| SSU72 | 0.337340 |
| UBE2I | 0.335501 |
| YY1 | 0.332398 |
| NCOR1 | 0.331547 |
| SNRNP70 | 0.330938 |
| ZNF207 | 0.325469 |
| BCLAF1 | 0.324426 |
| HNRNPH1 | 0.323872 |
| SON | 0.323490 |
Licensing: CC BY 4.0. You are fee to copy, redistribute, remix, transform and build upon all material, except for textbook figures from the Essentials.