Gene Details: PGM1
1 / 1
General Information
Gene Name: PGM1 (Phosphoglucomutase-1)
Synonym:
Short Names: PGM 1;
Alternative Names: Glucose phosphomutase 1;
Notes:
- Phosphoglucomutase 1 moves phosphate from the 1 carbon to the 6 carbon on glucose 1 phosphate. Plays a role in glycolysis.
- Deficiencies in this enzyme causes cardiomyopathy and hepatopathies.
Description from Dr.Glyco-GPT:
Warning: LLMs can generate factually incorrect information, as they simply predict the next word based on training data. Always verify LLM output by cross-checking with reliable sources!
Catalytic Activity

Reaction and Disease Links
EC # (IUBMB):
5.4.2.2
Brenda:
5.4.2.2
KEGG: 5236
Transcript levels (Cell lines and Single cell data) URL
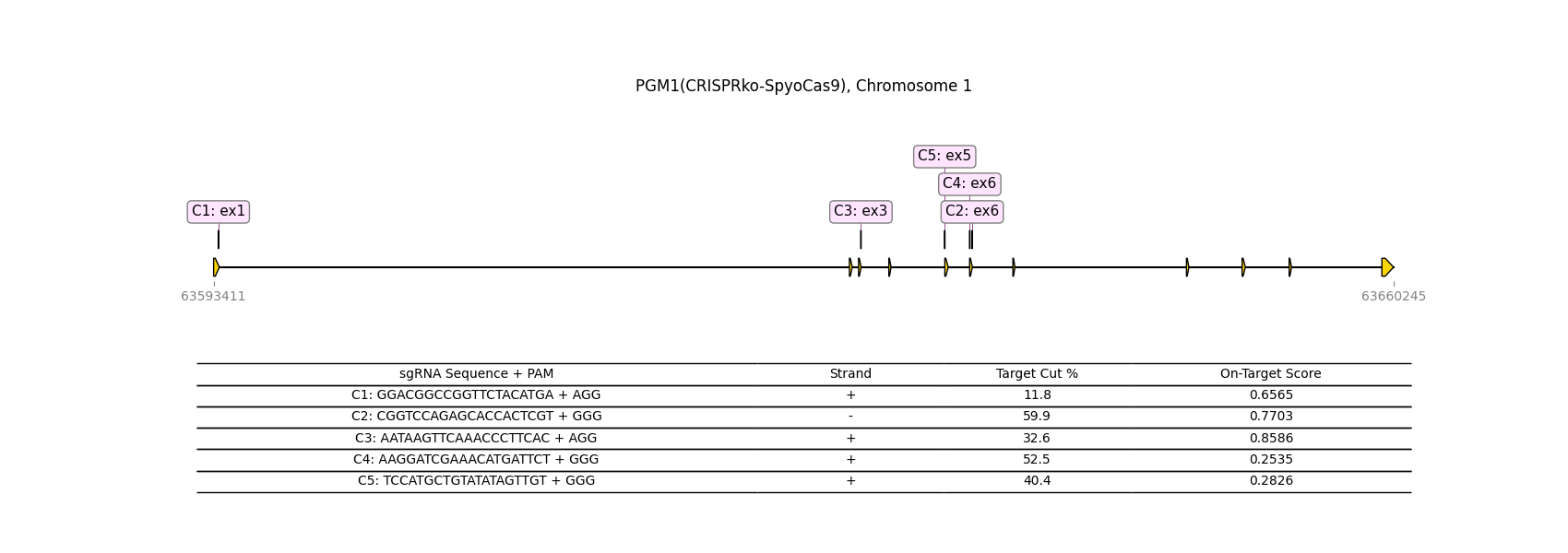
CRISPR-knockout
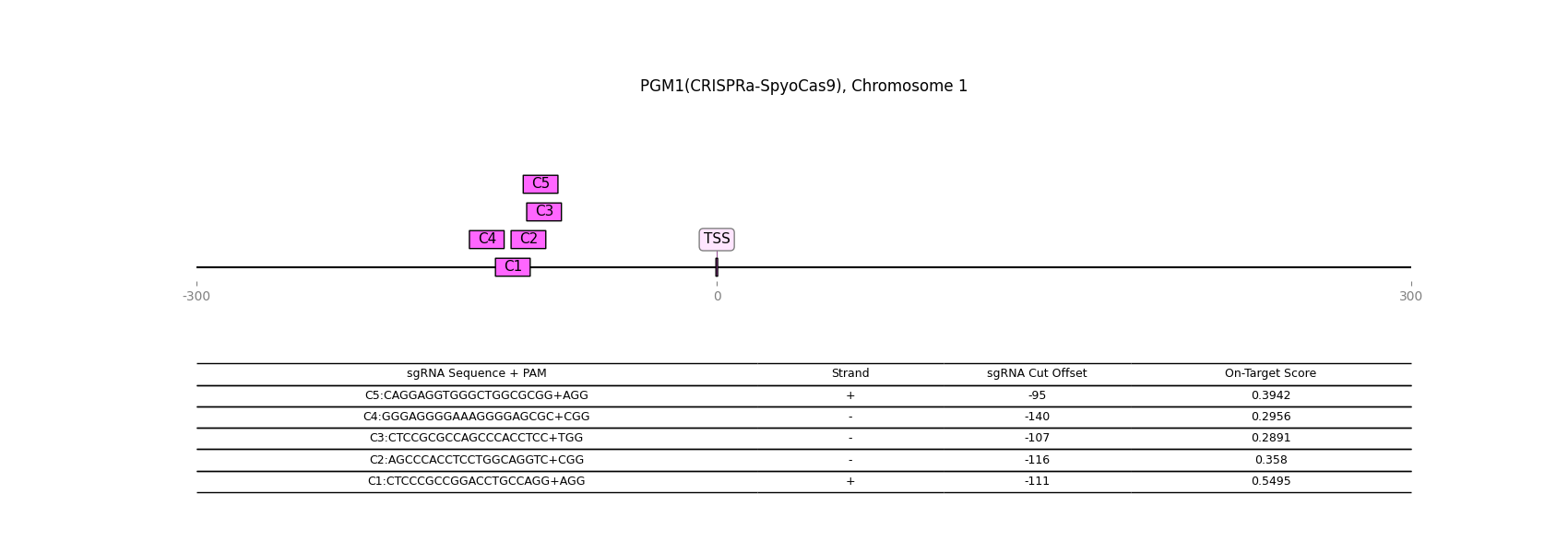
CRISPR-activation
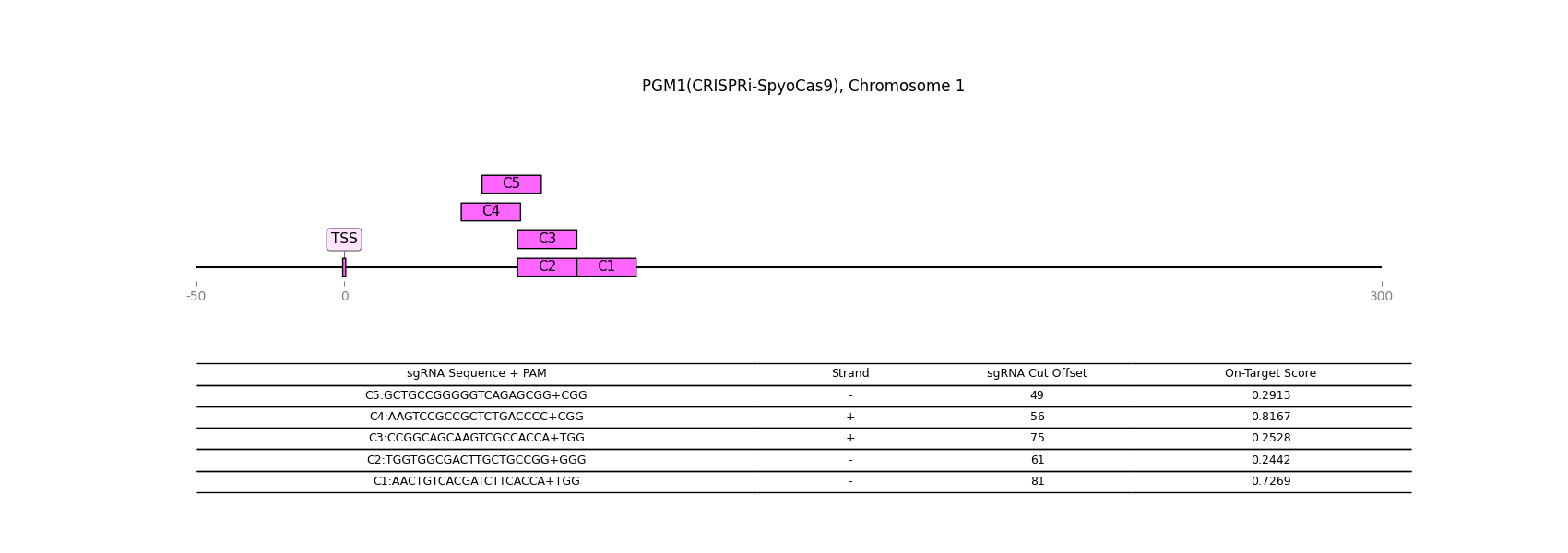
CRISPR-inactivation
Transcription factor-gene relationship (details at glycoTF page)
Top 10 TFs
| TF | Score |
|---|---|
| TCF25 | 0.717844 |
| UBE2I | 0.703326 |
| SSU72 | 0.702862 |
| YY1 | 0.690886 |
| XRCC5 | 0.683372 |
| SUMO1 | 0.679433 |
| NCOR1 | 0.676493 |
| SON | 0.673282 |
| PCBP1 | 0.672409 |
| HNRNPK | 0.671349 |
Licensing: CC BY 4.0. You are fee to copy, redistribute, remix, transform and build upon all material, except for textbook figures from the Essentials.